
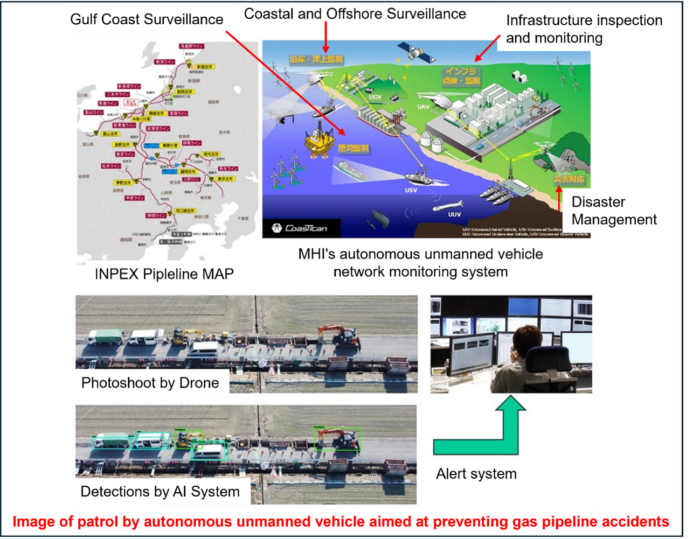
The four companies(INPEX Pipeline Corporation (INPEX PL), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (INPEX), INPEX Pipeline Corporation (INPEX PL), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd,(MHIMT), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. ) conducted a drone flight test using CoasTitan®, MHI’s autonomous unmanned vehicle network monitoring system, near a gas pipeline in Kashiwazaki City, Niigata Prefecture, owned and maintained by INPEX PL, a wholly owned subsidiary of INPEX.
CoasTitan® , MHI’s autonomous unmanned vehicle network monitoring system, was used to conduct a flight test. This demonstration test was conducted to confirm the safety of long-distance autonomous drone flights using LTE (Long Term Evolution) communication, which is the communication standard for mobile terminals, and to confirm road conditions and transmit images in real time using AI. The test successfully demonstrated the potential of autonomous drones for pipeline patrols. This confirmed the potential of autonomous unmanned pipeline patrols.
INPEX has more than 1,500 km of transportation pipelines in its domestic natural gas business, many of which are buried under public roads, and there is concern that unnotified road excavation work by INPEX or INPEX PL could result in accidents due to pipeline damage or gas leakage. There is concern that this could lead to accidents due to pipeline damage or gas leakage. For this reason, INPEX PL conducts vehicle patrols along the entire line to detect unidentified work in advance or at an early stage. The use of drones is expected to increase the frequency of patrols and further enhance security and stable supply based on this increase.
INPEX and MHI signed a “Memorandum of Understanding to Jointly Study Technological Issues in the Energy Sector” in 2016, and have been jointly studying the automation of pipeline patrols using autonomous unmanned vehicles, including drone flight demonstration tests, since FY2020. Specifically, MHI and MHIMT aim to use CoasTitan®, an autonomous unmanned vehicle network monitoring system developed by MHI’s Defense & Space segment, and MHIMT’s newly developed AI-based automatic road condition identification system to replace conventional visual checks by vehicle patrols. The system is expected to be an alternative to the conventional visual confirmation by vehicle patrols.
The demonstration test was conducted in anticipation of the enforcement of the revised Civil Aeronautics Law by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, which stipulates the requirements for Category III*1 drone flights, and was conducted under Category II*2 conditions. The demonstration test was conducted under Category II*2 conditions. The demonstration test was conducted as part of a joint research project with the Japan Energy, Metals and Minerals Corporation (JOGMEC).
In the future, we will conduct further long-distance autonomous flights, improve the object discrimination accuracy of AI models, and study measures for safe flights, aiming for early implementation of automated pipeline patrols by autonomous unmanned vehicles. In addition, we will continue to study the possibility of using the system to confirm the situation around pipelines and in response to requests from neighboring municipalities in the event of a disaster.
*1 Category III: Specified flights that take place in airspace and in a manner that requires permission or approval from the Minister of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism under the Civil Aeronautics Law.
*2 Category II: A specified flight that is conducted under the flight path of an unmanned aircraft with entry control measures (i.e., not flying over third parties).
Demonstration test outline
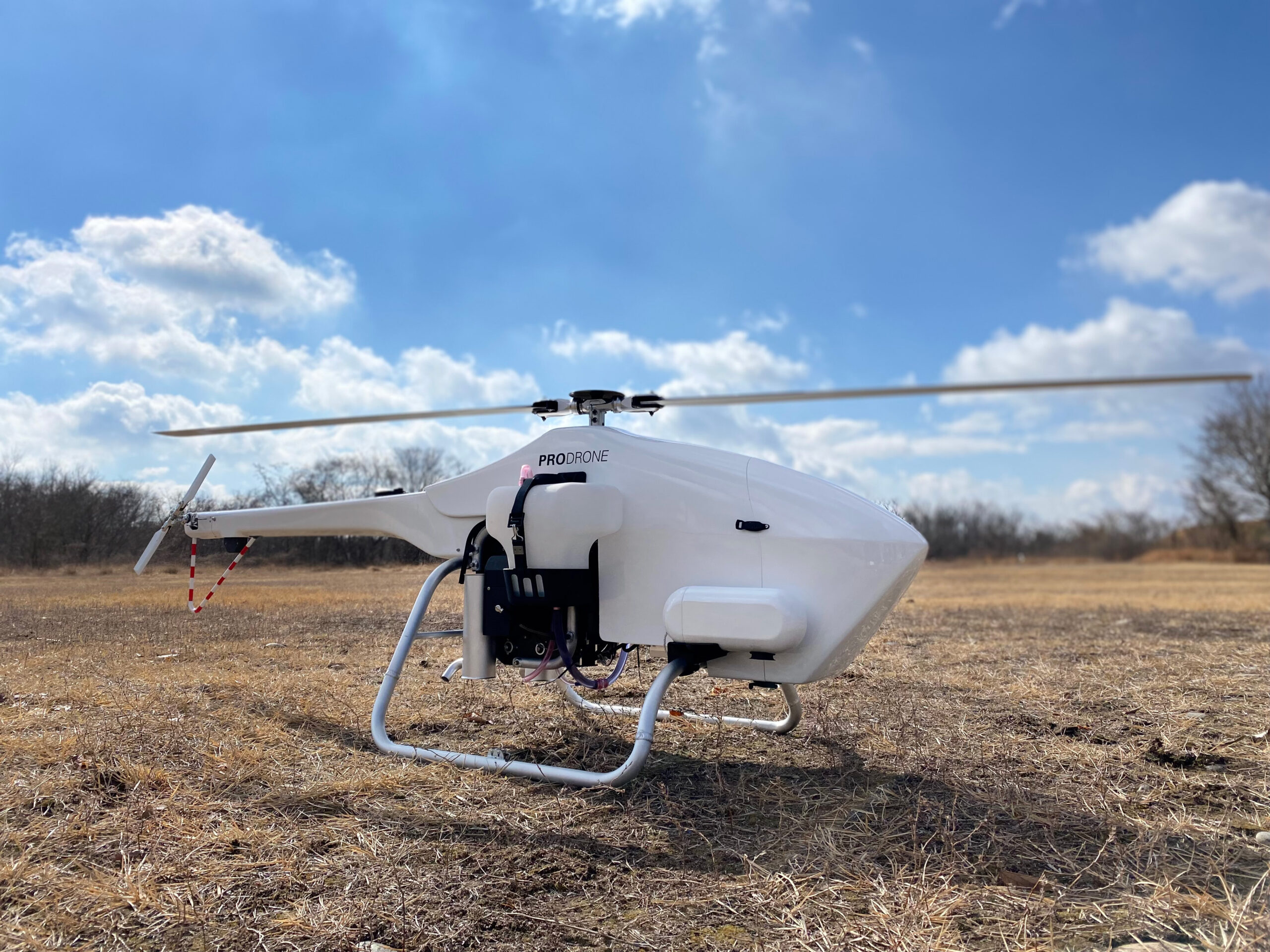
Demonstration test location: Near the INPEX gas pipeline in Kashiwazaki, Niigata Prefecture Flight Overview: Transmission of long-distance flight control status, photographed images, and results of construction status determination using LTE communications.
Depending on the flight route, a simulated road excavation site may be set up in the vicinity of the route to allow real-time image confirmation, and the drone on-board AI (AI equipped with an edge computer that learns road construction features and uses the AI to identify the road construction features) can be used to confirm images in real time.
Drone Type: Japanese-made single-rotor UAV (gasoline engine, capable of flying up to 100 km)
Identification of construction status: Automatic determination of road construction features such as backhoes and triangular cones using onboard AI, and transmission to the ground system via LTE communication.
About CoasTitan
CoasTitan® is an unmanned vehicle control system that enables a small number of operators to inspect and monitor (image capture) objects by networking autonomous unmanned vehicles equipped with various sensors (airborne/underwater/underwater/land-based).
CoasTitan is a registered trademark of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. in Japan.